Page014
Fig. 2.5 shows authorization using an Ubuntu Linux system. User Deckard has identified and authenticated himself, and logged into the system. He uses the Linux “cat” command to view the contents of “sebastian-address.txt.” Deckard is authorized to view this file, so permission is granted. Deckard then tries to view the file “/etc/shadow,” which stores the users’ password hashes. Deckard is not authorized to view this file, and permission is denied.
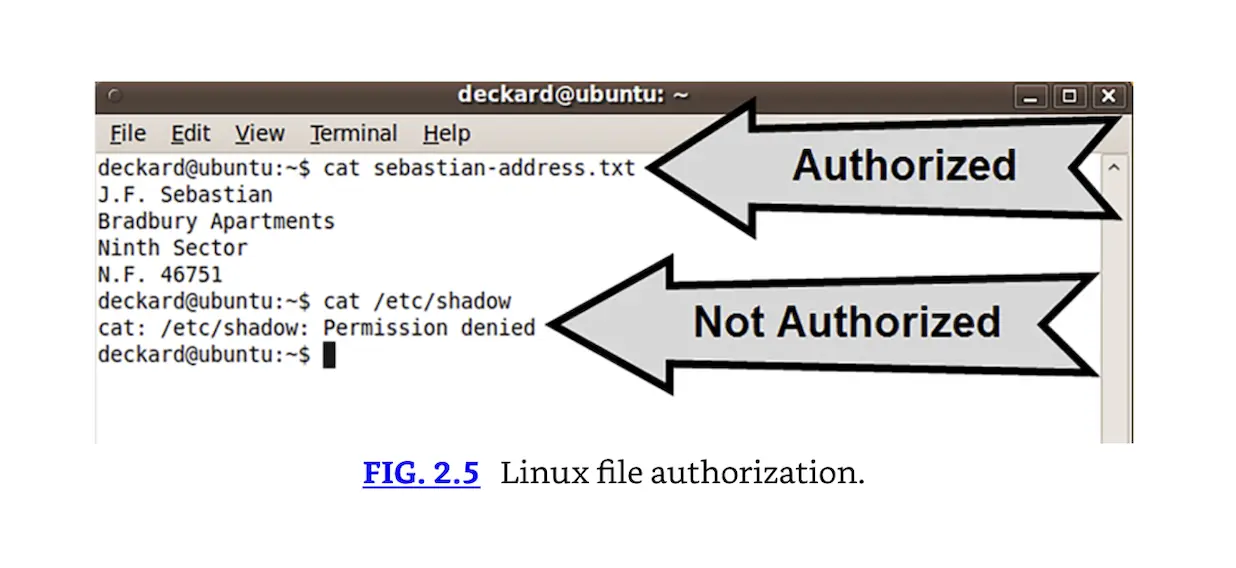 Linux file authorization.
Linux file authorization.
Accountability
Accountability holds users accountable for their actions. This is typically done by logging and analyzing audit data. Enforcing accountability helps keep “honest people honest.” For some users, knowing that data is logged is not enough to provide accountability: they must know that the data is logged and audited, and that sanctions may result from violation of policy.
The healthcare company Kaiser Permanente enforced accountability when it fired or disciplined over 20 workers for violating policy (and possibly violating regulations such as HIPAA) by viewing Nadya Suleman’s (aka the Octomom) medical records without a need-to-know. See this article for more details. Logging that data is not enough: identifying violations and sanctioning the violators is also required.
Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation means a user cannot deny (repudiate) having performed a transaction. It combines authentication and integrity: non-repudiation authenticates the identity of a user who performs a transaction, and ensures the integrity of that transaction. You must have both authentication and integrity to have non-repudiation: proving you signed a contract to buy a car (authenticating your identity as the purchaser) is not useful if the car dealer can change the price from $20,000 to $40,000 (violate the integrity of the contract).
Least Privilege and Need-to-Know
Least privilege means users should be granted the minimum amount of access (authorization) required to do their jobs, but no more. Need-to-know is more granular than least privilege: the user must need to know that specific piece of information before accessing it.
Sebastian is a nurse who works in a medical facility with multiple practices. His practice has four doctors, and Sebastian could treat patients for any of those four doctors. Least privilege could allow Sebastian to access the records of the four doctors’ patients, but not access records for patients of other doctors in other practices.
Need to know means Sebastian can access a patient’s record only if he has a business need to do so. If there is a patient being treated by Sebastian’s practice, but not by Sebastian himself, least privilege would allow access, but need-to-know would not.