Page223
Tunnel and Transport Mode
IPsec can be used in tunnel mode or transport mode. Tunnel mode provides confidentiality (ESP) and/or authentication (AH) to the entire original packet, including the original IP headers. New IP headers are added (with the source and destination addresses of the IPsec gateways). Transport mode protects the IP data (layers 4–7) only, leaving the original IP headers unprotected. Both modes add extra IPsec headers (an AH header and/or an ESP header). Fig. 5.24 shows the differences between tunnel and transport modes.
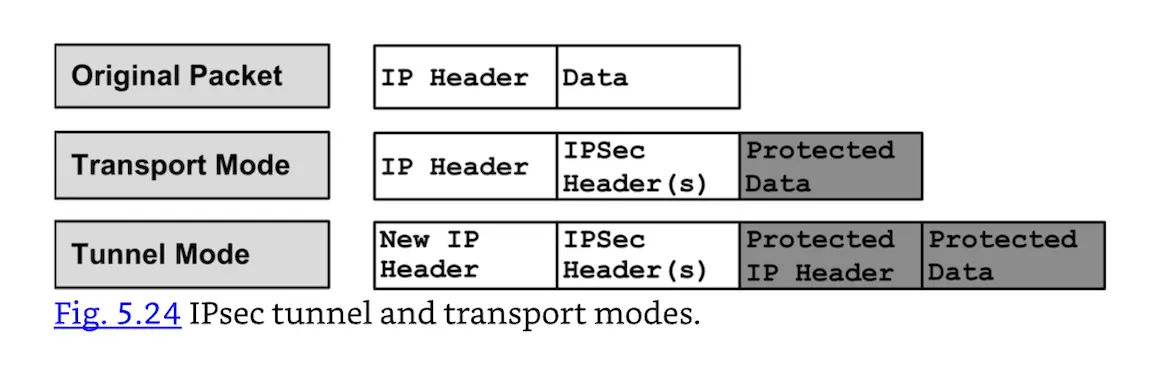 IPsec tunnel and transport modes.
IPsec tunnel and transport modes.
SSL and TLS
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) was designed to protect HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) data: HTTPS uses TCP port 443. TLS (Transport Layer Security) 1.0 was equivalent to SSL version 3.1. The current version of TLS is 1.3, described in RFC 8446.
Though initially Web-focused, SSL or TLS may be used to encrypt many types of data and can be used to tunnel other IP protocols to form VPN connections. SSL VPNs can be simpler than their IPsec equivalents: IPsec makes fundamental changes to IP networking, so installation of IPsec software changes the operating system (which requires super-user privileges). SSL client software does not require altering the operating system. Also, IPsec is difficult to firewall; SSL is much simpler.
Remote Access
In an age of telecommuting and the mobile workforce, secure remote access is a critical control. This includes connecting mobile users via methods such as DSL or Cable Modem, security mechanisms such as callback, and newer concerns such as instant messaging and remote meeting technology.
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) was an earlier attempt to provide digital service via “copper pair,” the POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) prevalent in homes and small offices around the world. This is called the “last mile,” providing high-speed digital service via the (historically copper pair) last mile has been a longstanding challenge.
ISDN devices are called terminals. ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) service provides two 64 K digital channels (plus a 16K signaling channel) via copper pair. A PRI (Primary Rate Interface) provides twenty-three 64K channels, plus one 16K signaling channel.
ISDN never found widespread home use; it was soon eclipsed by DSL and cable modems. ISDN is commonly used for teleconferencing and videoconferencing.