Page237
Salts
A salt allows one password to hash multiple ways. Some systems (like modern UNIX/Linux systems) combine a salt with a password before hashing. While storing password hashes is superior to storing plaintext passwords, “The designers of the UNIX operating system improved on this method (hashing) by using a random value called a ‘salt’. A salt value ensures that the same password will encrypt differently when used by different users. This method offers the advantage that an attacker must encrypt the same word multiple times (once for each salt or user) in order to mount a successful password-guessing attack”.
This makes rainbow tables far less effective (if not completely ineffective) for systems using salts. Instead of compiling one rainbow table for a system that does not use salts, such as Microsoft LAN Manager (LM) hashes, thousands, millions, billions or more rainbow tables would be required for systems using salts, depending on the salt length.
Password Management
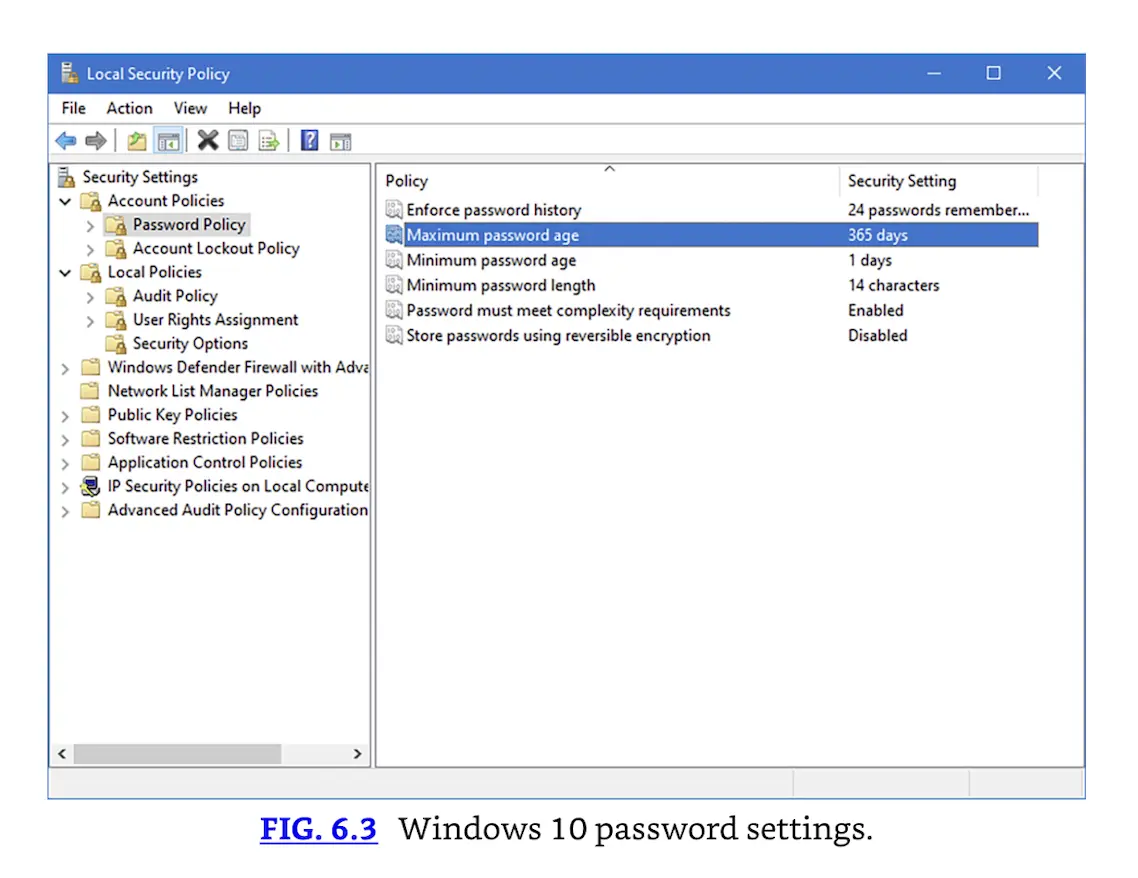 Windows 10 password settings.
Windows 10 password settings.
Managing passwords in a Microsoft Windows environment is fairly straightforward. The IT or InfoSec staff determines the organizational policy and implements that policy through the DC. Center for Internet Security’s Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Benchmark includes the following recommendations regarding a standard password policy:
- Password history = set to remember 24 passwords
- Maximum password age = 365 days
- Minimum password age = 1 day (this is because users do not cycle through 24 passwords to return immediately to their favorite)
- Minimum password length = 14 characters
- Passwords must meet complexity requirements = true
- Store password using reversible encryption = false [3]
The difficulties arise when users do not properly create or secure the passwords they choose. For example, it is not uncommon for users to write down passwords and store them in wallets, address books, cell phones, and even sticky notes posted on their monitors.
Password Control
Controlling passwords is a concern for management as well as the IT security professional. One problem is complex passwords are harder to remember, which can lead to other security issues. Users who write passwords down and leave them in an insecure place (such as under a keyboard or stored in a wallet, purse, or unlocked desk) can undermine the entire security posture of a system.