Page239
Asynchronous Dynamic Token
Asynchronous dynamic tokens are not synchronized with a central server. The most common variety is challenge-response tokens. Challenge-response token authentication systems produce a challenge, or input for the token device. Then the user manually enters the information into the device along with their PIN, and the device produces an output. This output is then sent to the system. The system is assured that the user is authenticated because the response is tied to the challenge, a specific token, the encryption algorithm used by the token, and the user’s PIN.
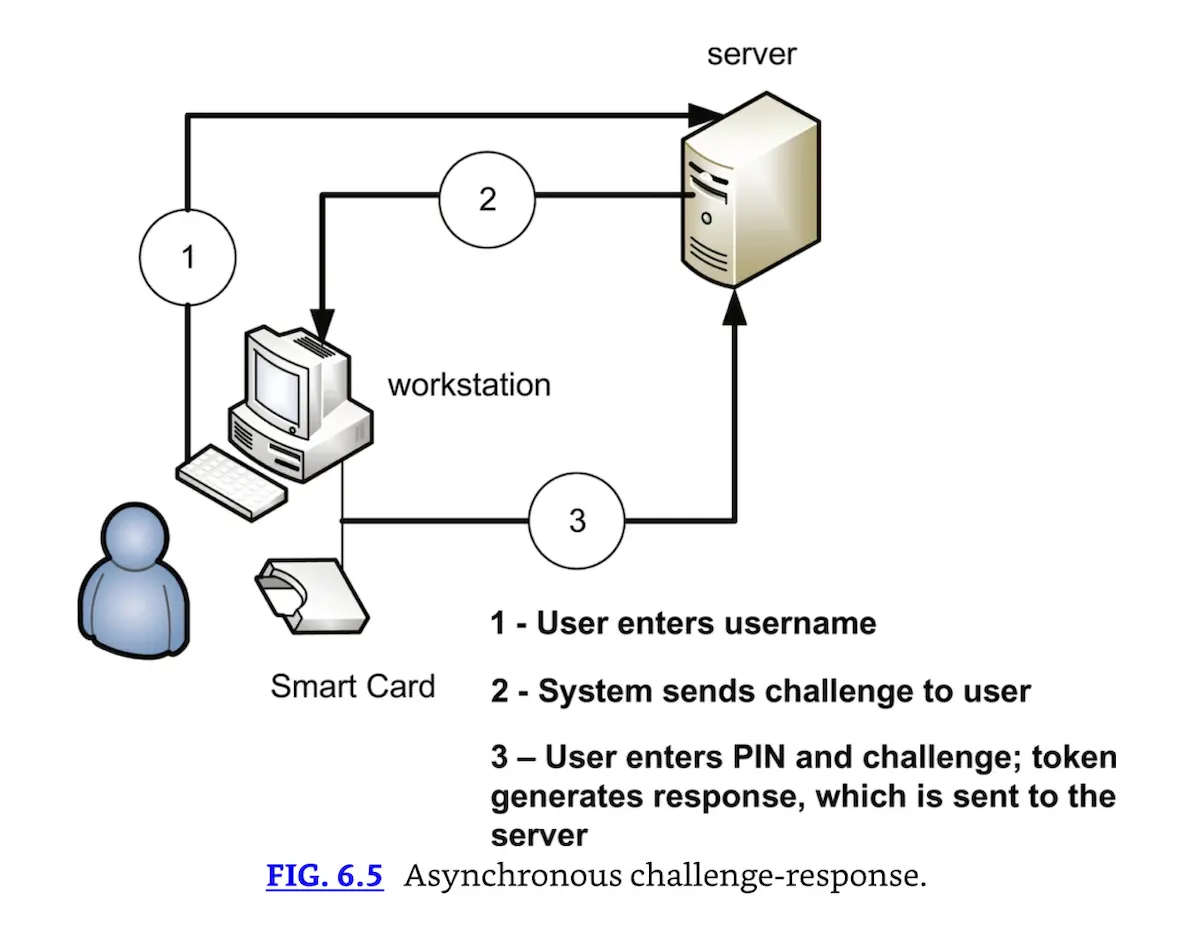 Asynchronous challenge-response.
Asynchronous challenge-response.
Combining access control types is recommended and can provide greater security for access control. Using more than one type of access control is referred to as strong authentication or multifactor authentication.
Type 3 Authentication: Something You Are
Type 3 authentication (something you are) is biometrics, which uses physical characteristics as a means of identification or authentication. The term “biometric” derives from the Greek words “bios” (life) and “metric” (measurement). Biometrics may be used to establish an identity, or to authenticate (prove an identity claim). For example: an airport facial recognition system may be used to establish the identity of a known terrorist, and a fingerprint scanner may be used to authenticate the identity of a subject (who makes the identity claim, and then swipes his/her finger to prove it).
Because biometrics is associated with the physical traits of an individual, it is more difficult for that individual to forget, misplace, or otherwise lose control of that access capability. Biometrics may be used to provide robust authentication, but care should be given to ensure appropriate accuracy and to address any privacy issues that may arise as a result.
Biometrics should be reliable, and resistant to counterfeiting. The data storage required to represent biometric information (called the template or the file size) should be relatively small (it will be accessed upon every authentication): 1000 bytes or less is typical (much less for some systems, like hand geometry).