Page372
DevOps
Traditional software development was performed with strict separation of duties between the developers, quality assurance teams, and production teams. Developers had hardware that mirrored production models, and test data. They would hand code off to the quality assurance teams, who also had hardware that mirrored production models, as well as test data. The quality assurance teams would then hand tested code over to production, who had production hardware and real data.
In the old (less agile) model: developers had no direct contact with production, and in fact were strictly walled off from production via separation of duties.
DevOps is a more agile development and support model, echoing the agile programming methods we learned about previously in this chapter, including Sashimi and Scrum. DevOps is “the practice of operations and development engineers participating together in the entire service lifecycle, from design through the development process to production support” [15].
DevSecOps
DevSecOps is an agile method that integrates information security into the development process. Security is involved in every step. The DevSecOps Manifesto outlines the goals:
- Leaning in over Always Saying “No”
- Data & Security Science over Fear, Uncertainty and Doubt
- Open Contribution & Collaboration over Security-Only Requirements
- Consumable Security Services with APIs over Mandated Security Controls & Paperwork
- Business Driven Security Scores over Rubber Stamp Security
- Red & Blue Team Exploit Testing over Relying on Scans & Theoretical Vulnerabilities
- 24 × 7 Proactive Security Monitoring over Reacting after being Informed of an Incident
- Shared Threat Intelligence over Keeping Info to Ourselves
- Compliance Operations over Clipboards & Checklists [16]
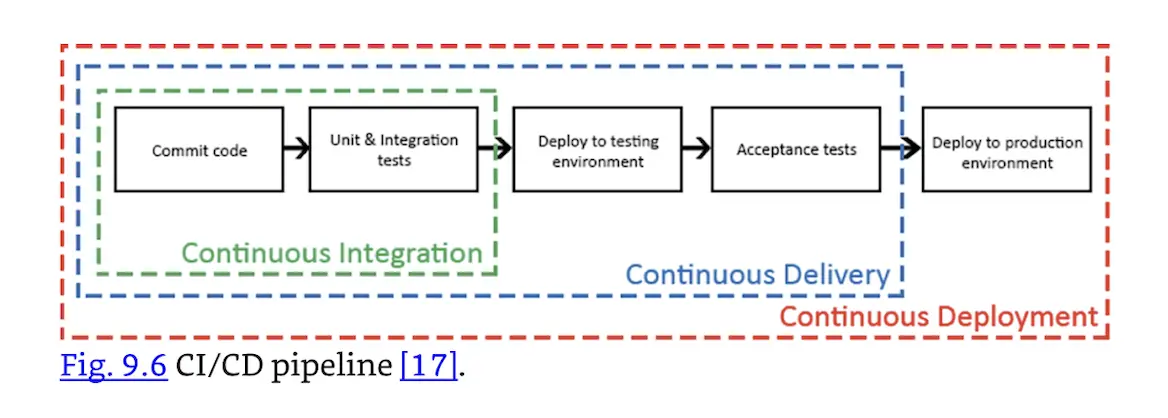
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) is an agile methodology that focuses on rapidly deploying code updates via pipelines. It is one of the core DevSecOps practices. NIST describes CI/CD:
A unique concept that DevSecOps introduces in the process workflow is the concept of “pipelines”. With pipelines, there is no need to individually write jobs for initiating/executing each stage of the process. Instead, there is only one job that starts from the initial stage, automatically triggers the activities/tasks pertaining to other stages (both sequential and parallel), and creates an error-free smart workflow.
The pipeline in DevSecOps is called the CI/CD pipeline based on the overall tasks it accomplishes and the two individual stages it contains. CD can denote either the continuous delivery or continuous deployment stage. Depending on this latter stage, CI/CD can involve the following tasks:
- Build, Test, Secure, and Deliver—the tested modified code is delivered to the staging area.
- Build, Test, Secure, Deliver, and Deploy—the code in the stage area is automatically deployed [17].
Fig. 9.6 from NIST, shows the CI/CD pipeline.
 CI/CD pipeline [17].
CI/CD pipeline [17].